Mastering the Fair Value Gap Indicator for Better Trading Strategies
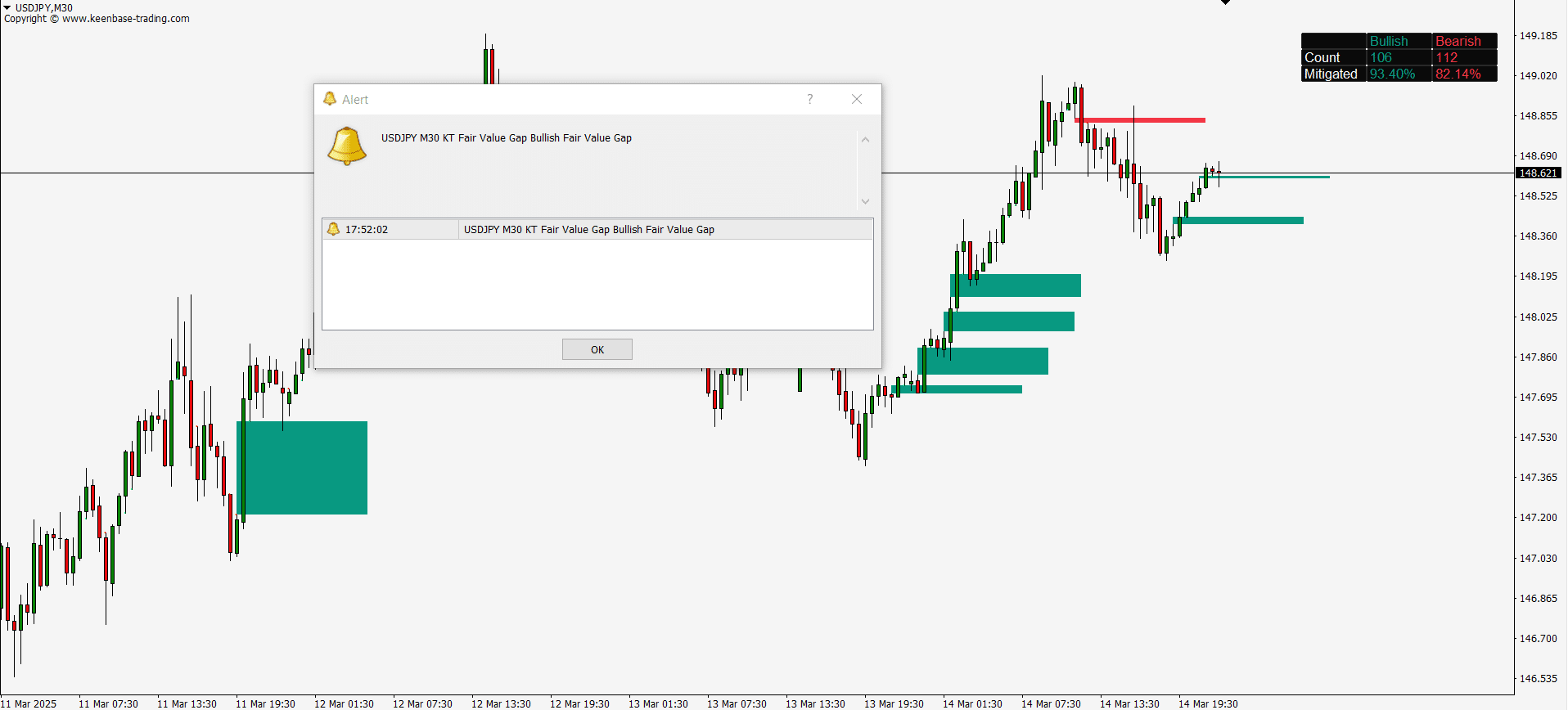
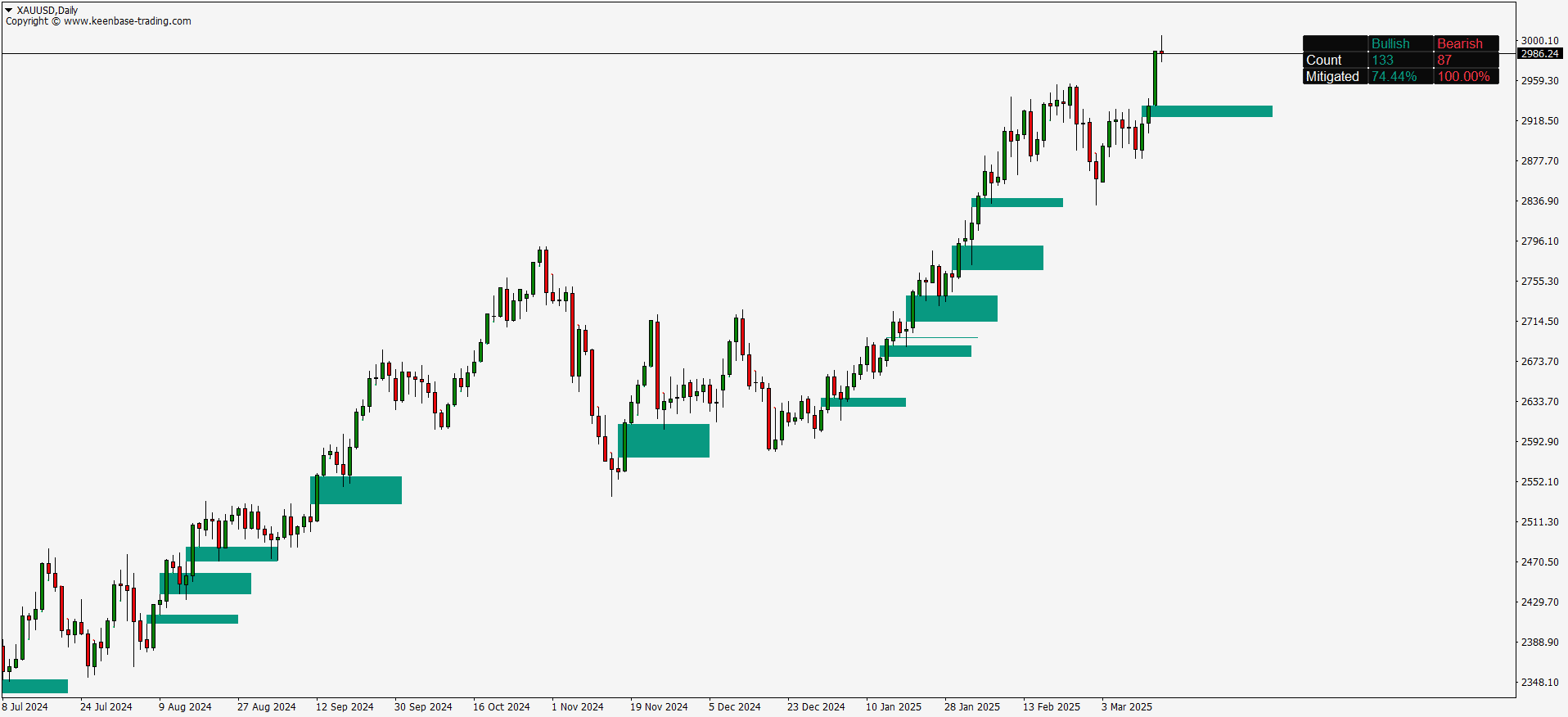
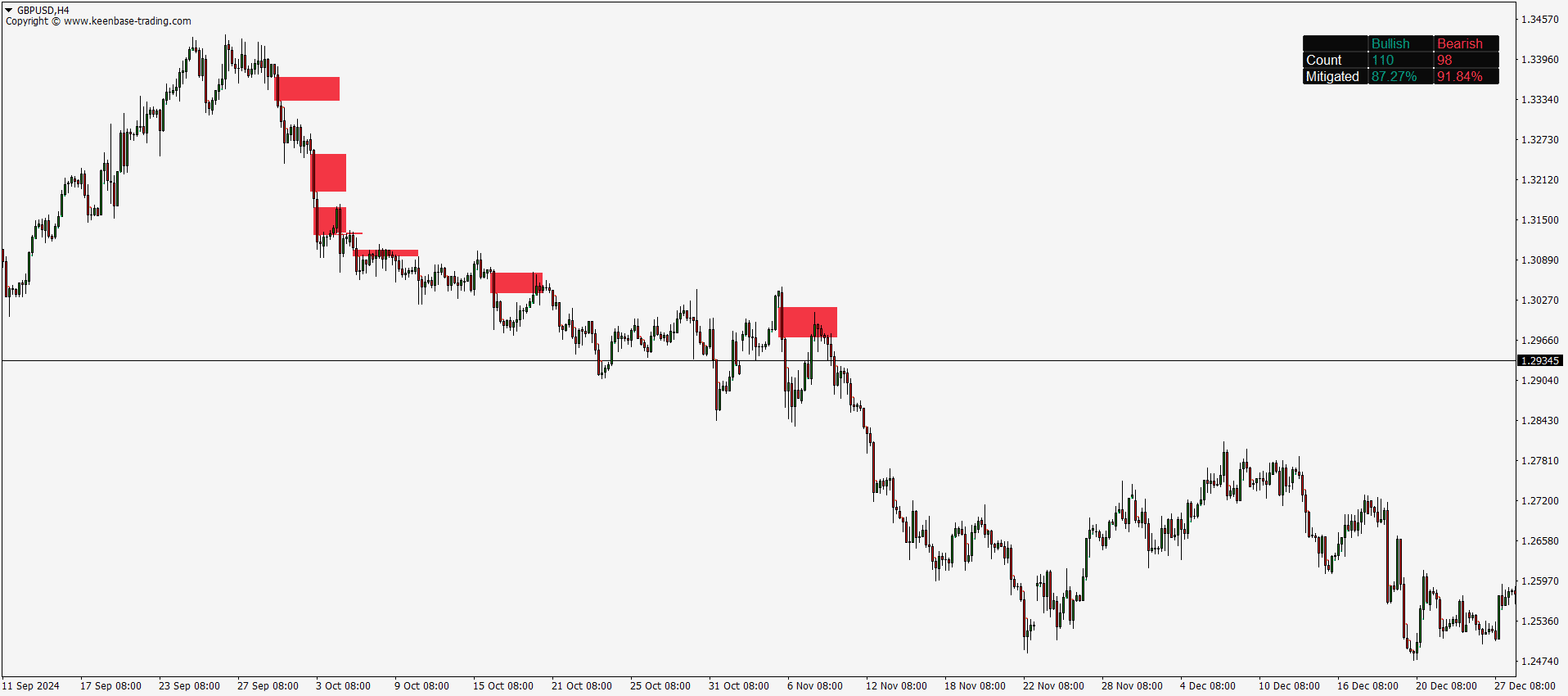
The KT FVG indicator highlights gaps between candles that reveal moments of price imbalance. These gaps often point to market inefficiencies and potential trade setups. Understanding how to use them can improve your timing and lead to smarter decisions in your trading.
Key Takeaways
- Spot Market Imbalances: It helps identify inefficiencies in price action, offering traders potential setups for strong price movements.
- Combine with Other Tools: For better accuracy and fewer false signals, use the indicator alongside tools like volume analysis and moving averages.
- Prioritize Risk Management: Incorporate stop-loss orders and proper position sizing to manage risk effectively when trading based on Fair Value Gaps.
Price action traders place special importance on Fair Value Gaps, as they reveal moments when buying and selling forces are out of balance—often leading to sharp price moves. Spotting these imbalances can help traders anticipate future price action and make more informed, strategic decisions.
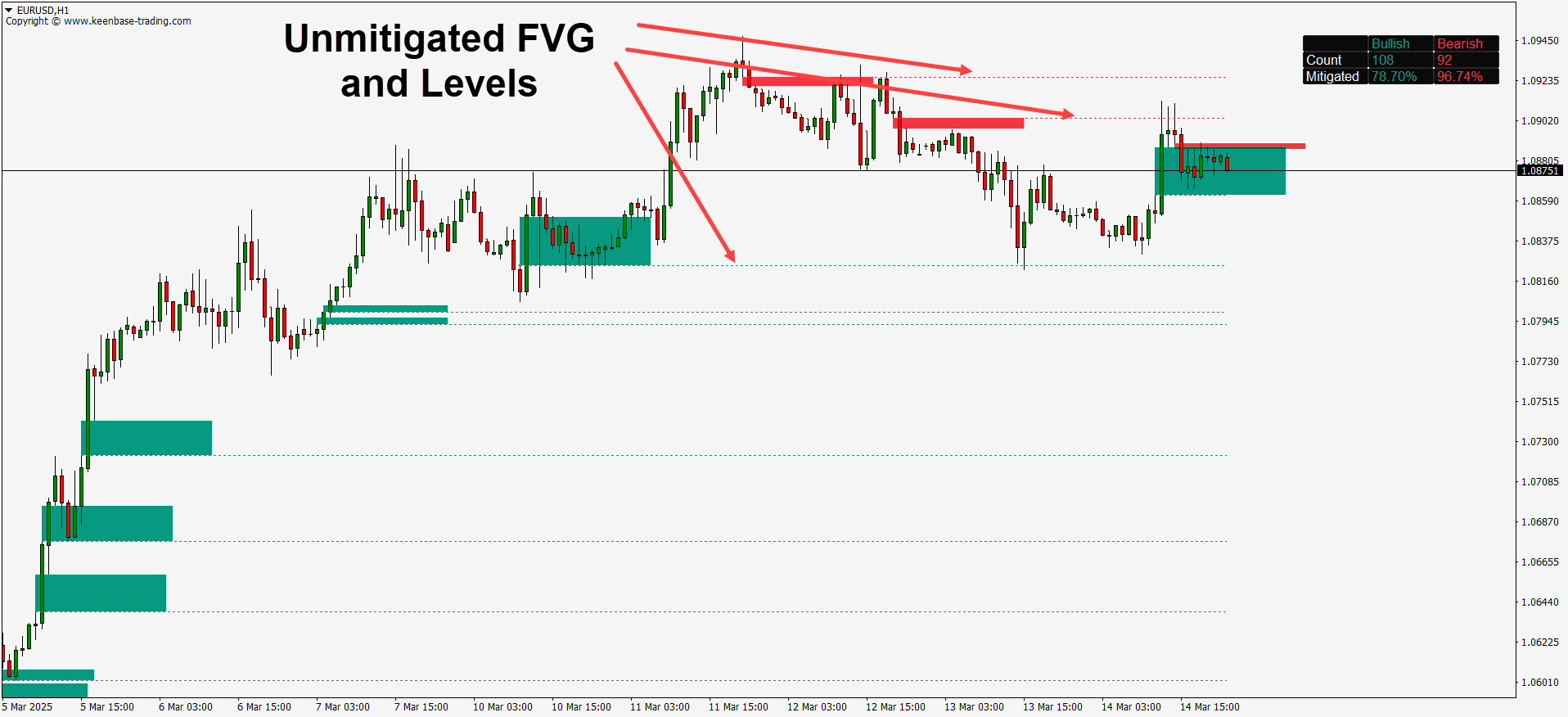
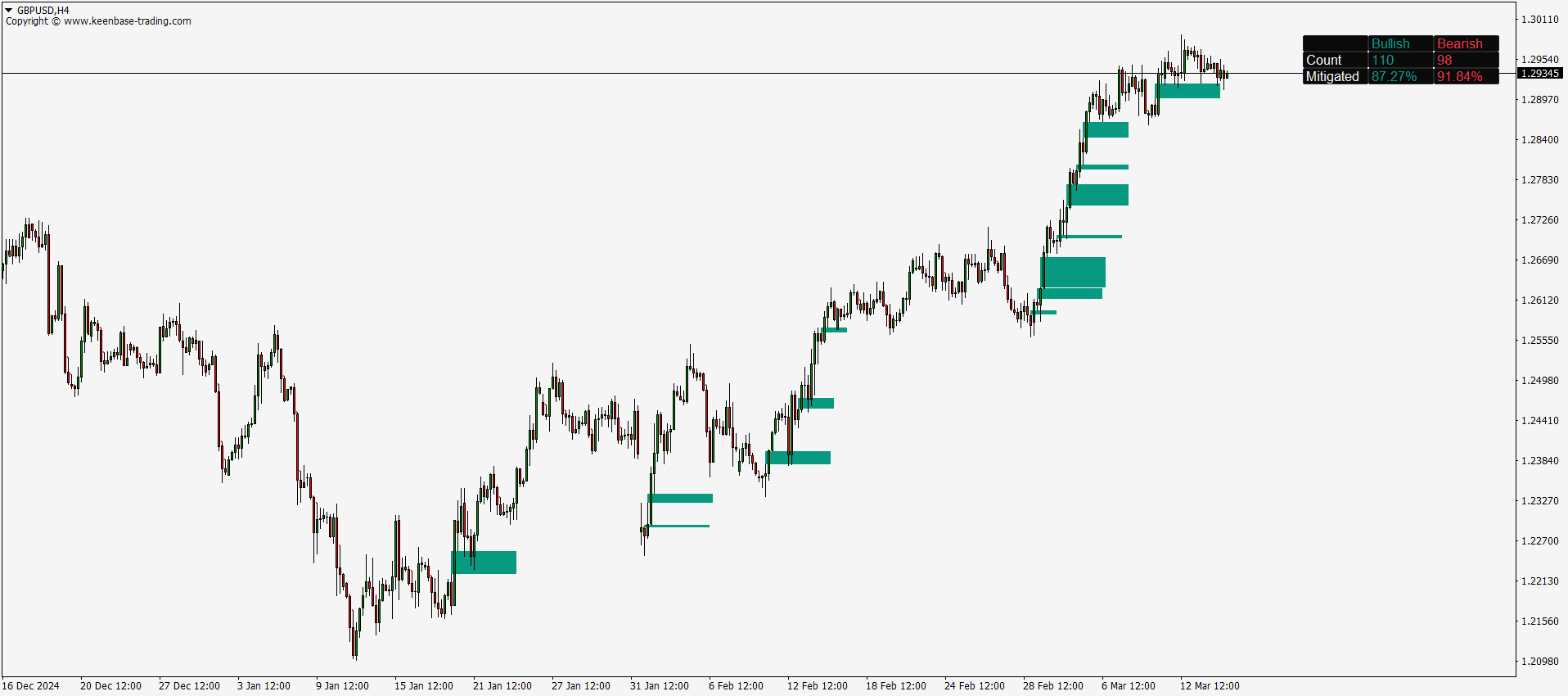
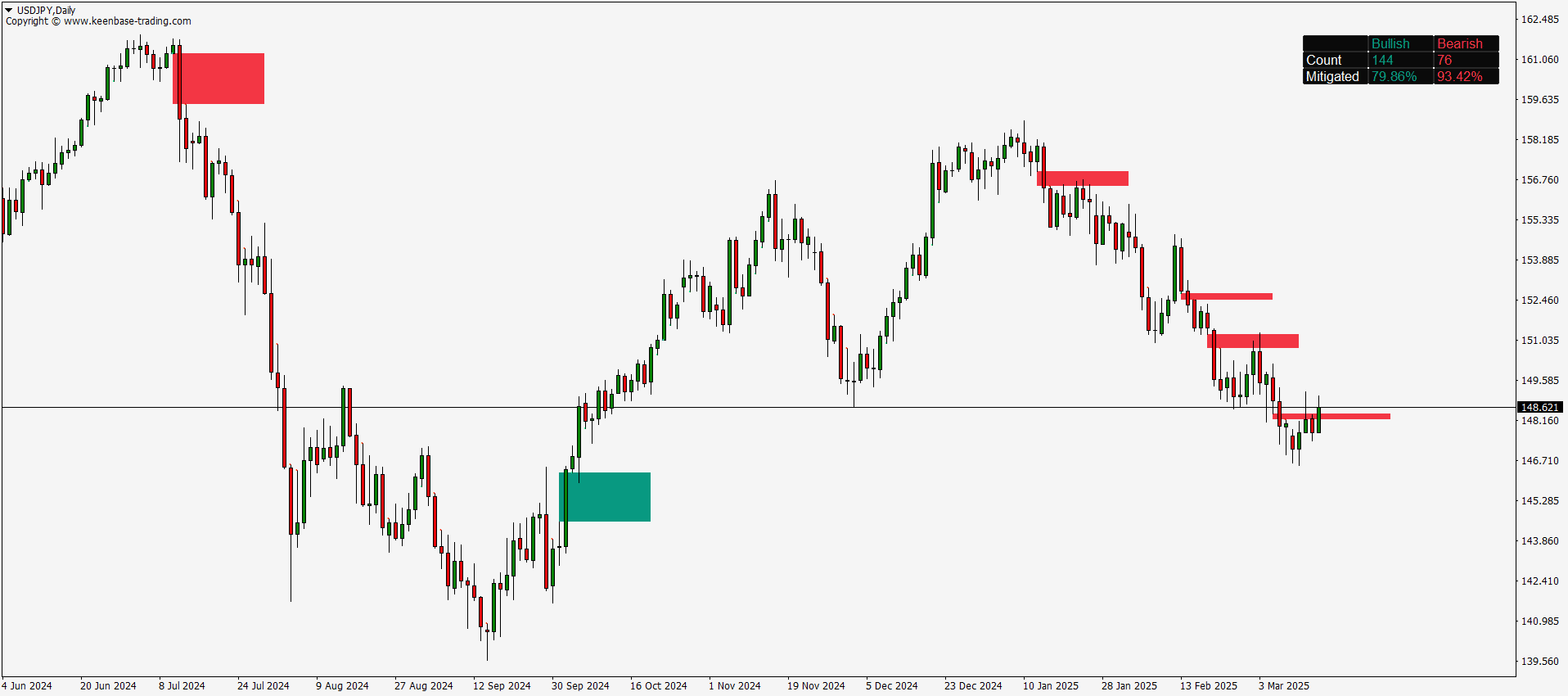
Fair Value Gaps typically appear in a three-candle formation, where a large candle does not fully overlap with the wicks of its neighboring candles. This unique pattern stands out on the chart, signaling potential trade setups. While skilled traders may spot these gaps visually, using a dedicated FVG indicator makes the process faster and more accurate by automatically highlighting them.
Despite their advantages, trading with Fair Value Gaps isn't foolproof. Market volatility can lead to unexpected outcomes. To get the most from this strategy, traders should combine it with solid analysis, proper risk management, and a deep understanding of price behavior.
Timeframe Flexibility:
While FVGs appear on all timeframes, many traders prefer intraday charts like 1, 5, or 15 minutes to spot short-term reversals and precise entry points.
Understanding Bullish & Bearish FVG Structures
- Bullish Fair Value Gaps occur when there’s no overlap between the high of the left candle and the low of the right candle, with a strong green candle in the middle. These gaps suggest potential upward momentum.
- Bearish Fair Value Gaps are formed when the low of the left candle and the high of the right candle do not overlap, with a strong red candle in the center. If the price closes above the gap's upper boundary, it’s considered invalid. Otherwise, price entering this zone may reverse downward.
Using Fair Value Gaps in Trading Strategies
A well-planned Fair Value Gap strategy involves waiting for price to return to the gap zone before entering a trade. For bullish setups, traders look for price to drop into the gap before going long. For bearish setups, the opposite applies—waiting for a rally into the gap before entering short.
Entry and Exit
Patience is key. One of the most common mistakes is jumping in too early, which often leads to poor entries. Entry signals are strongest when the price cleanly retraces into the gap zone.
Exit points can be set once the gap is filled, allowing traders to lock in profits. To stay protected, always use stop-loss levels based on nearby structure or just beyond the gap zone, especially in volatile conditions.
Limitations of Fair Value Gaps
While Fair Value Gaps can highlight valuable trade setups, they’re not without limitations. One common mistake is assuming every gap will be filled—this can lead to false signals and poor entries. Traders should wait for confirmation and apply strict entry/exit rules to avoid acting on assumptions.
Market conditions also play a critical role. Economic news, geopolitical events, or shifts in investor sentiment can override the technical picture, making some gaps unreliable. Always consider the broader market context when using this strategy.
Practical Examples of Fair Value Gap Trading Setups
Seeing fair value gap setups in action helps traders apply the concept with more confidence. Below are two simple examples that show how to enter, manage, and exit FVG-based trades.
Example 1: Bullish FVG Trade
After identifying a bullish fair value gap on the chart, wait for the price to retrace into the gap zone. Once bullish confirmation appears (e.g., a strong bullish candle or support reaction), consider entering a long position.
- Entry: When price taps into the gap zone.
- Stop-Loss: Just below the lower boundary of the gap.
- Take-Profit: At a recent swing high or after the gap is filled.
Example 2: Bearish FVG Trade
Spot a bearish fair value gap following a strong downward move. Wait for price to rally back into the gap area. If selling pressure reappears, it could be an opportunity to go short.
- Entry: Near the top of the gap.
- Stop-Loss: Just above the upper boundary.
- Take-Profit: At a prior low or when the gap closes.
Combining FVGs with Other Indicators
Pairing the FVG with other indicators can strengthen your overall strategy. For example:
- Moving Averages: Use moving averages to confirm the prevailing trend. When a bullish FVG appears above a rising moving average, it adds weight to the long setup. Similarly, bearish FVGs below a declining average can signal stronger short opportunities.
- Volume Analysis: High volume during the formation or retest of an FVG adds credibility to the signal. It helps confirm the buyer-seller imbalance and reduces the risk of false entries.
These combinations add layers of confirmation, helping you filter out weak setups and improve decision-making.
Final Thoughts
The KT Fair Value Gap Indicator simplifies the process of identifying market inefficiencies and turning them into actionable trade setups. While it offers a powerful edge, success still depends on disciplined execution, proper risk management, and adapting to market conditions.
Combine this indicator with other tools, stay patient with entries, and always consider the broader context. With the right approach, Fair Value Gaps can become a key part of your trading strategy.