We hope you enjoy reading this blog post.
Become a Pro Trader by using our fine-tuned Indicators and Expert Advisors.
What is Trade Management in Forex? Key Strategies for Success

In the dynamic and fast-paced world of Forex trading, where global currencies fluctuate due to a myriad of economic and geopolitical factors, the ability to manage trades effectively is often what separates successful traders from the rest.
Trade management is the strategic process of monitoring, controlling, and adjusting active positions to maximize potential profits and mitigate risks.
It goes beyond placing trades; it is the art of steering them through market volatility toward a favorable outcome.
Effective trade management is indispensable for navigating the complexities of the Forex market.
Even the most well-researched trading strategies can fail without a robust plan for managing trades once they are active.
Factors like sudden market fluctuations, unexpected economic data releases, or shifts in market liquidity can turn profitable positions into losing trades.
By adopting sound trade management practices, traders not only protect their capital but also improve their chances of achieving consistent profitability.
This article discusses the critical components of Forex trade management, offering insights into personalized trading plans, advanced risk management techniques, emotional discipline, and performance analysis.
We will also explore how to align trade management strategies with your trading style, optimize risk-reward ratios, and adapt to changing market conditions.
For both aspiring and seasoned traders, mastering trade management is an essential step toward long-term success in the foreign exchange market.
What is Trade Management in Forex
Forex trade management strategies are the strategic process of overseeing active trades to maximize profits and minimize risks, basically having a higher risk-reward ratio.
In a high-volatility market, currency prices fluctuate massively due to economic and geopolitical events, effective trade management acts as a safeguard, helping traders maintain control over their running positions.
Some tools work as a filter for the trend like trend filter indicators that can help you filter the noise in the market
It encompasses a range of actions, such as setting stop-loss and take-profit levels, adjusting position sizes, and monitoring trades in real time to react to changing market dynamics.
The role of trade management extends beyond simply managing individual trades; it is important for achieving consistent performance and aligning trading activities with long-term goals.
Without a structured plan for managing trades, even the most well-researched strategies can fail when faced with unforeseen market fluctuations.
For example, a sudden release of unfavorable economic data or an announcement of geopolitical instability can cause sudden price movements that derail a promising trade.
Proactive trade management ensures that traders can adapt to such scenarios, protecting their capital and securing gains.
Why is Trade Management Crucial?
1. Navigating Market Volatility
With price movements driven by a wide range of factors, including geopolitical developments, central bank decisions, and unexpected economic data releases, market trends are easily affected.
Trade management equips traders with the tools to adapt to these dynamic conditions.
Incorporating stop-loss orders can help limit losses during sharp market reversals while adjusting position sizes in response to increased market volatility ensures that risk exposure remains within acceptable limits.
2. Maintaining Consistency
Consistency in trading is achieved through disciplined adherence to a well-defined trading plan.
Setting precise rules for entry and exit points, coupled with maintaining a favorable risk-reward ratio (e.g., 1:2 or higher), helps traders focus on strategic objectives rather than reacting emotionally to market movements.
Predetermining a profit target and stop-loss level for each trade minimizes the temptation to alter decisions based on short-term price fluctuations.
3. Avoiding Costly Mistakes
Poor trade management often leads to errors such as overleveraging, chasing losses, or holding onto unprofitable positions in the hope of recovery.
These mistakes can deplete trading capital rapidly, undermining even the most robust strategies.
A disciplined trade management framework addresses these pitfalls by emphasizing risk control measures.
Trade management is not just a skill—it’s an essential part of a trader’s toolkit.
By mastering these fundamentals, traders can navigate the complexities of the Forex market with confidence, consistency, and resilience.
Risk Management in Forex Trading
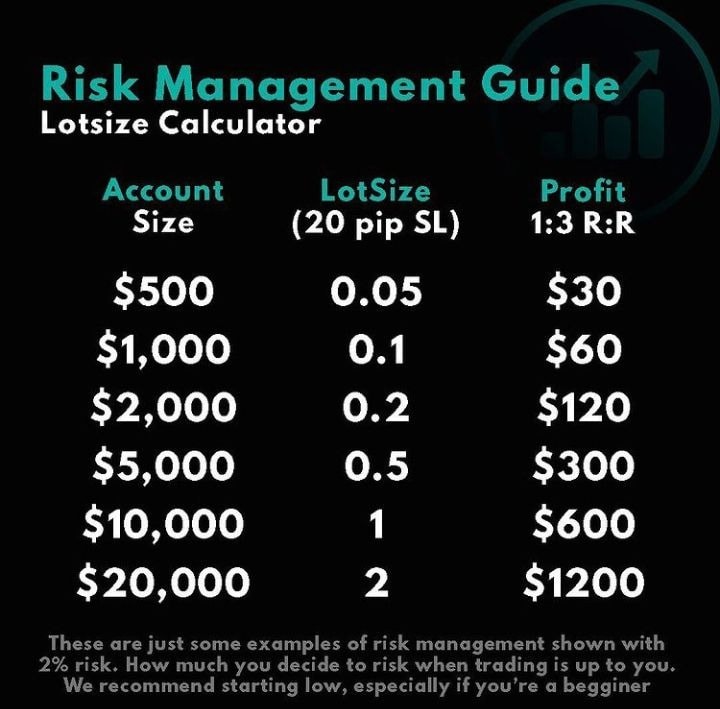
Risk management is the backbone of sustainable Forex trading, ensuring that potential losses are minimized while maximizing growth opportunities. Key techniques include:
Stop-Loss Orders: Automatically close a trade when it reaches a predetermined loss level, preventing emotional decision-making and limiting downside risk. or you can use this tool Auto SL TP EA
Limit Orders: Lock in profits by automatically closing a trade when a target price is hit.
Leverage Management: While leverage amplifies both profits and losses, responsible use is critical. For example, using 1:10 leverage instead of 1:100 significantly reduces the risk of account depletion during volatile market conditions.
Balancing risk and potential profit involves calculating risk per trade and maintaining discipline, ensuring that no single trade jeopardizes the trader’s overall account.
Setting Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Levels
Determining appropriate levels for stop-loss and take-profit orders requires analyzing market conditions and identifying key levels of support and resistance. Traders should:
Use stop-loss levels that align with their risk tolerance and account size. If you are risking 1–2% of account capital per trade is a widely accepted standard.
Set take-profit levels based on achievable risk-reward ratios, ensuring that potential rewards outweigh risks.
Avoiding overexposure is vital; This involves diversifying positions and maintaining smaller trade sizes during periods of heightened market uncertainty.
Managing Leverage and Risk
Leverage is a double-edged sword in Forex trading. Responsible traders:
Use low leverage ratios (e.g., 1:10 or 1:05) to reduce exposure to market fluctuations.
Incorporate leverage into a broader strategy that includes strict stop-loss orders and position sizing to manage overall risk exposure effectively.
Position Sizing and Risk-Reward Ratio
Position sizing determines how much capital to allocate to a trade, ensuring that risk remains manageable. A common formula is:
Position Size= (Account Balance× Risk Per Trade)/ (Stop-loss in pips x pip value)
With a $10,000 account risking 1% per trade and a stop-loss of 50 pips at a pip value of $10, the position size would be:
Position Size= (10,000x 0.01)/ (50x 10)= 2 Lots.
Precise calculations ensure that no trade exposes the account to excessive risk, preserving capital for long-term trading.
Setting Risk-Reward Ratios
Maintaining a minimum 1:2 risk-reward ratio means risking $1 to potentially earn $2. This approach ensures that even with a 50% success rate, traders remain profitable over time.
Adjusting risk-reward ratios to align with market conditions—such as increasing targets during trending markets or scaling back during consolidation phases—improves adaptability and sustainability.
Emotional Discipline and Market Adaptability

Emotions play a major role in trading, often undermining judgment and prompting impulsive decisions during volatile market periods.
To maintain control, traders can benefit from integrating mindfulness techniques, such as deep-breathing exercises or short meditation sessions, before executing trades.
These practices help cultivate a calm and focused mindset, reducing the likelihood of emotionally driven actions.
Additionally, traders can use pre-trade checklists, which enforce a systematic review of entry and exit conditions, ensuring decisions align with their strategy rather than emotional impulses.
Another overlooked tool is implementing psychological journaling alongside a trading journal.
By documenting feelings and thoughts during trades, traders can identify recurring emotional patterns—such as overconfidence after wins or frustration during losing streaks—and develop personalized strategies to address them.
Adaptability to changing market conditions requires not only monitoring technical and fundamental indicators but also understanding market sentiment analysis, such as shifts in trader positioning or reactions to geopolitical events.
Utilizing tools like sentiment indices or analyzing open interest data from trading platforms provides insights into how the broader market is likely to behave, allowing traders to adjust accordingly.
Trade Performance Analysis and Continuous Improvement
Consistent success in Forex trading requires regular performance analysis and a commitment to continuous improvement.
This involves maintaining a trading journal, leveraging performance metrics, and learning from past trades to refine strategies and decision-making processes.
Maintaining a Trading Journal
A trading journal is an invaluable tool for tracking and analyzing trades.
By recording details such as entry and exit points, position sizes, market conditions, and trade outcomes, traders can identify recurring patterns and areas for improvement.
For example, a trader might notice that trades executed during high-volatility periods tend to be less successful, prompting adjustments to their strategy.
A detailed journal highlights broader trends in a trader’s performance over time.
Using Performance Metrics
Performance metrics offer a quantitative way to evaluate trading strategies. Key metrics include:
Win Rate: The percentage of profitable trades relative to total trades, which helps assess the effectiveness of entry and exit strategies.
Risk-Reward Ratio: The average profit per trade compared to the average loss, indicating the efficiency of risk management.
Profit Factor: The total profit divided by total loss, offering an overall measure of strategy profitability.
Regularly reviewing these metrics enables traders to identify strengths and weaknesses in their approach, ensuring data-driven improvements.
Learning from Past Trades
Historical trade data serves as a powerful resource for refining strategies. By analyzing past trades, traders can pinpoint mistakes, such as improper position sizing or poorly timed entries, and develop solutions to prevent them in the future.
Additionally, understanding the reasons behind successful trades allows traders to replicate winning strategies under similar market conditions.
By maintaining a trading journal, leveraging performance metrics, and continuously learning from past trades, traders can enhance their strategies and build a framework for sustained success in the Forex market.
Final Thoughts
Trade management is the cornerstone of successful Forex trading, bridging the gap between strategy development and consistent execution.
It encompasses a comprehensive approach to risk control, emotional discipline, and continuous improvement, all of which are critical for navigating the dynamic and often unpredictable Forex market.
By mastering the fundamentals—such as setting effective stop-loss and take-profit levels, calculating precise position sizes, and maintaining a favorable risk-reward ratio—traders can safeguard their capital while optimizing profitability.
Take Your Trading to Next Level
Take Your Trading to Next Level
You Might Also Like:


